<< Web Picks >> Why Gambling was Popular in Ancient Rome
Submitted by Andy_B on Monday, 22 June 2020 Page Views: 4343
Resources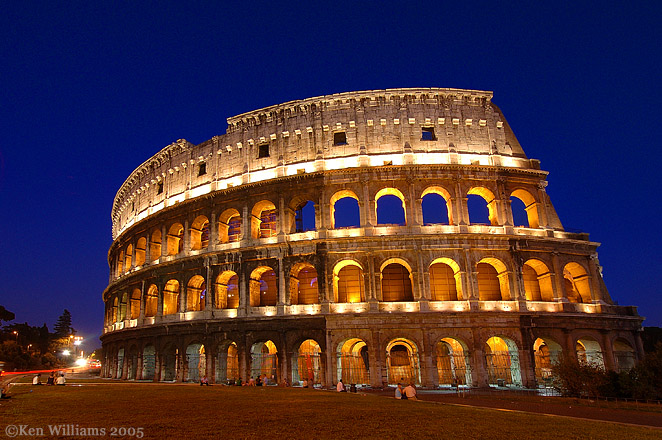
The Social Classes
Almost everyone gambled in ancient Rome. Every social class it seems, from a humble slave through to the emperor, would bet regularly. However, women were not permitted to participate in gambling games that involved men. It was only during the Bona Dea Festival that they were allowed to legally place a wager as the event was held especially for women.The Evolution of Popular Games in Rome
In ancient Rome, there were only two games available: dice only or dice and a board. The boards commonly had 36 squares and featured different symbols, which ranged from letters, crosses, and leaves. Players would then throw three dices on the board, and a combination of three sixes secured a winning throw. The dice were made from various materials, such as bone, ivory, and even glass. They were similar in style to modern-day dice, as they featured six sides and dots from numbers 1 to 6. As soldiers often had much time on their hands, they were partial to gambling with a game board, which they would often bring to their military posts. Many of these boards were discovered throughout the centuries in Italy, North Africa, and England.
The dice were made from various materials, such as bone, ivory, and even glass. They were similar in style to modern-day dice, as they featured six sides and dots from numbers 1 to 6. As soldiers often had much time on their hands, they were partial to gambling with a game board, which they would often bring to their military posts. Many of these boards were discovered throughout the centuries in Italy, North Africa, and England.Another popular option was one of the earliest versions of backgammon, known to Romans as “The Game of Twelve Signs.” It required three cubic dice, and every player had 15 pieces to play with. Those without a game board would often scratch or engrave squares onto pavements or the steps of buildings. These engravings are still visible today on some courthouses, public bathhouses, and temples. Knucklebones was also a popular game to place a wager on. It was based on skill, as five bones were thrown into the air, and a player had to catch every bone before they hit the floor.
These rudimentary games were so much different from modern times when players can choose from a variety of entertainment options. For instance, it now seems normal to place an online bet on a sporting event or step inside a glamorous casino such as the Bellagio in Las Vegas or Wynn Palace in Macau to play card games. There are also no physical limitations in placing a wager in the modern world, as it’s possible to visit sites like 888 to play online casino games on any internet-enabled device. It now seems normal to place an online bet on a sporting event or step inside a glamorous kubet casino such as the Bellagio in Las Vegas or Wynn Palace in Macau to play card games. The first versions of these prevalent card games were brought to Europe in the 14th century from the Mameluke empire of Egypt, long after the fall of the Western Roman Empire. But regardless of the historical period, some form of “Lady Luck” has always been present in the gambling culture.
Goddess Fortuna – The Patroness of Gamblers
 Despite prohibiting gambling, Emporer Augustus was a strong believer in the goddess Fortuna and regularly played games of chance
Despite prohibiting gambling, Emporer Augustus was a strong believer in the goddess Fortuna and regularly played games of chanceLife in ancient Rome was heavily influenced by ancient Greece, and this included much of their belief system. For instance, it was common for many Romans to pray and present offerings to the goddess Fortuna, with the hope of receiving good luck when placing a wager.
Fortuna was viewed by many as a symbol of fate, and her history was often connected to stories of chance. Gamblers who wanted to increase their luck and enjoy great wealth often chose to worship the goddess. Augustus Caesar was a firm believer in Fortuna, as he strongly believed she had selected him as one of her favourites. During his dinner parties, he was known for auctioning tickets for prizes that were unequal in value. To avoid the wrath of his guests, he reminded them it was Fortuna who determined the prize they received, and not him.
Gambling Laws in Rome
Despite gambling proving popular with Romans from all backgrounds, the pastime was generally prohibited in ancient Rome throughout the republican and imperial era. In addition to the Bona Dea festival, Romans were legally allowed to gamble during Saturnalia, a week-long festival that honoured the God Saturn. The event also allowed slaves to place a wager at the same table as their master. If, however, a Roman was caught gambling outside of the celebrations, they would receive a fine.Before the pastime was forbidden, many Romans would often gamble at home or a public house, such as a private home or tavern. The introduction of the laws didn’t deter the Romans from gambling. As mentioned, Augustus himself was fond of gambling and did not allow his own laws to deter him from the action. He reportedly lost 30,000 sesterces when betting on a match at the Colosseum. The sum was thirty times more than an average Roman soldier’s annual salary. He was so passionate about placing a wager that many writers often commented on his weakness for various games.
Gambling was outlawed during Emperor Augustus’ reign, as he had the aim of introducing it as a holy activity that was not susceptible to tax. However, as many of Rome’s arenas were privately owned and not controlled by the emperor, the venues were still taxed.
Cheating
The popularity of dice games led to many dealers attempting to scam players out of their cash, which commonly led to fights. In fact, Pompeii features graffiti on its walls that states, “I am skilled enough to win without cheating.” Nowadays new technologies have been implemented in Slotbox Casino to monitor the player to avoid cheating in the game.It’s also possible to view a cartoon that was painted on the floor in the ruins of a tavern. The first cartoon features two men sitting with a game board on their knees. The first man states “EXSI,” which translates in English to “I’m out,” and the second man says, “NON TRIA DV AS EST,” which means “Not three points but two.” The second cartoon then depicts the two men standing in a fighting pose. The tavern keeper also states, “ITIS FORIS RIXSATIS,” translating to “leave my place if you want to fight.”
Trick coins from ancient Rome have also been discovered. A piece of iron was inserted into a coin to disturb its balance before it was re-joined together to create the illusion of a genuine coin. Some Romans also placed iron or lead weights into dice to determine the outcome.
While gambling is a historic pastime, it has undoubtedly changed throughout the centuries, thanks to the introduction of various games and new technologies. However, it is as popular today as it was with Romans, as it can provide some much-needed escapism.
With many thanks to Ken Williams, Mo Pie, 888 Casino and Jansold for their kind help and support of this article, including their lovely photos. (Dice photo by Mo Pie is Creative Commons)


 We would like to know more about this location. Please feel free to add a brief description and any relevant information in your own language.
We would like to know more about this location. Please feel free to add a brief description and any relevant information in your own language. Wir möchten mehr über diese Stätte erfahren. Bitte zögern Sie nicht, eine kurze Beschreibung und relevante Informationen in Deutsch hinzuzufügen.
Wir möchten mehr über diese Stätte erfahren. Bitte zögern Sie nicht, eine kurze Beschreibung und relevante Informationen in Deutsch hinzuzufügen. Nous aimerions en savoir encore un peu sur les lieux. S'il vous plaît n'hesitez pas à ajouter une courte description et tous les renseignements pertinents dans votre propre langue.
Nous aimerions en savoir encore un peu sur les lieux. S'il vous plaît n'hesitez pas à ajouter une courte description et tous les renseignements pertinents dans votre propre langue. Quisieramos informarnos un poco más de las lugares. No dude en añadir una breve descripción y otros datos relevantes en su propio idioma.
Quisieramos informarnos un poco más de las lugares. No dude en añadir una breve descripción y otros datos relevantes en su propio idioma.